
Optimizing your nutrition is key when living with interstitial lung disease. Some are risk for malnourishment, as lung disease can cause a hypermetabolic state. Others may be prey to the side effects of medications that cause weight gain. For some, having trouble breathing can make such a daily activity as eating a great challenge. There are some general tips that we encourage in individuals with interstitial lung disease. Below, you will find many other tips shared from our colleagues at the UCSF Nutrition Counseling Clinic.
UCSF Nutrition Counseling Clinic
You can see a dietitian at our NCC for more individualized nutrition counseling:
- Get a referral from your doctor.
- Check with your insurance that they cover the visit.
- Call 415-353-2291 to make an appointment.
General Guidelines for Eating Healthy
General diet modifications for ILD patients
- Eat 5-6 small meals instead of 3 large meals.
- Last meal no later than 7 pm or 3 hours before bedtime.
- Sit up after meals.
- Avoid high-fat foods.
- Limit other foods that increase reflux.
Achieve and maintain a healthy body mass index (BMI). Aim for a BMI of around 20 to 30. Maintaining a healthy weight is important for people with lung disease. Excess weight can increase shortness of breath and puts a strain on your
Eat a balanced diet with plenty of protein, fresh fruits
Eat several small meals of high nutritional value. Eating a large meal can leave you feeling too full and can restrict your lungs from fully inflating, making it more difficult to breathe. Eating three smaller meals and three snacks a day makes the stomach less full, leaving more room for your lungs to expand. Make every calorie you eat beneficial to your body.
Eat your main meal early in the day so you'll have more energy throughout the day.
If you wear oxygen, be sure to use it during meals. The body requires lots of oxygen for eating and digestion.
Limit sodium intake. Sodium can cause fluid retention, which may interfere with breathing. You should especially watch your sodium consumption if you're taking prednisone or if you have high blood pressure or heart problems. Try to get no more than 2,400 mg of sodium per day.
Foods especially high in sodium include:
Table salt, the most common source of sodium in our diets. One teaspoon of table salt contains 2,000 mg of sodium.
Processed foods such as:
- Anchovies and sardines
- Chips, crackers, pretzels
and nuts - Frozen dinners
- Ketchup
- Luncheon meats, ham, hot dogs, bacon, sausage
and salt pork - Many
breads and bakery goods - Many canned foods such as soups, vegetables, pork and beans
and tomato products - Many
cereals - Monosodium glutamate (MSG)
- Mustard
- Soy sauce
- Steak sauce
Sodium also occurs naturally in foods. Unsalted, unprocessed foods such as fresh fruits, vegetables, meats
Include fiber in your diet. Fiber aids the digestion process and bowel function and should be incorporated into your daily meals. Fiber is found in whole wheat, oat and bran products, fruits and vegetables and beans. The only problem with some high-fiber foods is the excess gas they may produce, which could increase shortness of breath.
Fiber supplements that contain soluble fiber:
• Citrucel
• Nutrisource fiber
Avoid foods that cause gas and bloating. If the foods on this list bother you, eat less of them:
- Apples (raw)
- Asparagus
- Beans (pinto, kidney, black, navy)
- Broccoli
- Brussel sprouts
- Cabbage
- Carbonated drinks
- Cauliflower
- Corn
- Cucumbers
- Melons
- Onions (raw)
- Peas (split, black-eyed)
- Peppers
- Pimentos
- Radishes
- Rutabagas
- Turnips
Limit caffeinated drinks. Caffeine can interfere with some medications and can cause restlessness or nervousness.
Limit alcohol. Alcohol interferes with a good night's rest.
If you have acid reflux, limit foods that increase acidity in the stomach. Spicy foods, caffeine
For some ways to structure your meal plans, here are some additional resources:
Mediterranean Diet
Most of your foods will come from:
• Vegetables
• Fruits
• Whole grains and cereals
• Nuts, seeds, and nut butter
• Beans and lentils
• Fish and other seafood
• Olive oil
• Garlic, herbs, spices
About 2-3 times per week, choose:
• Poultry: chicken, turkey
• Low-fat dairy: yogurt, cheese, milk
• Eggs
• Soy protein: tofu, tempeh
Limit to 2-3 times per month:
• Red meat
• Animal fats: butter, lard, and cream
Plate Method
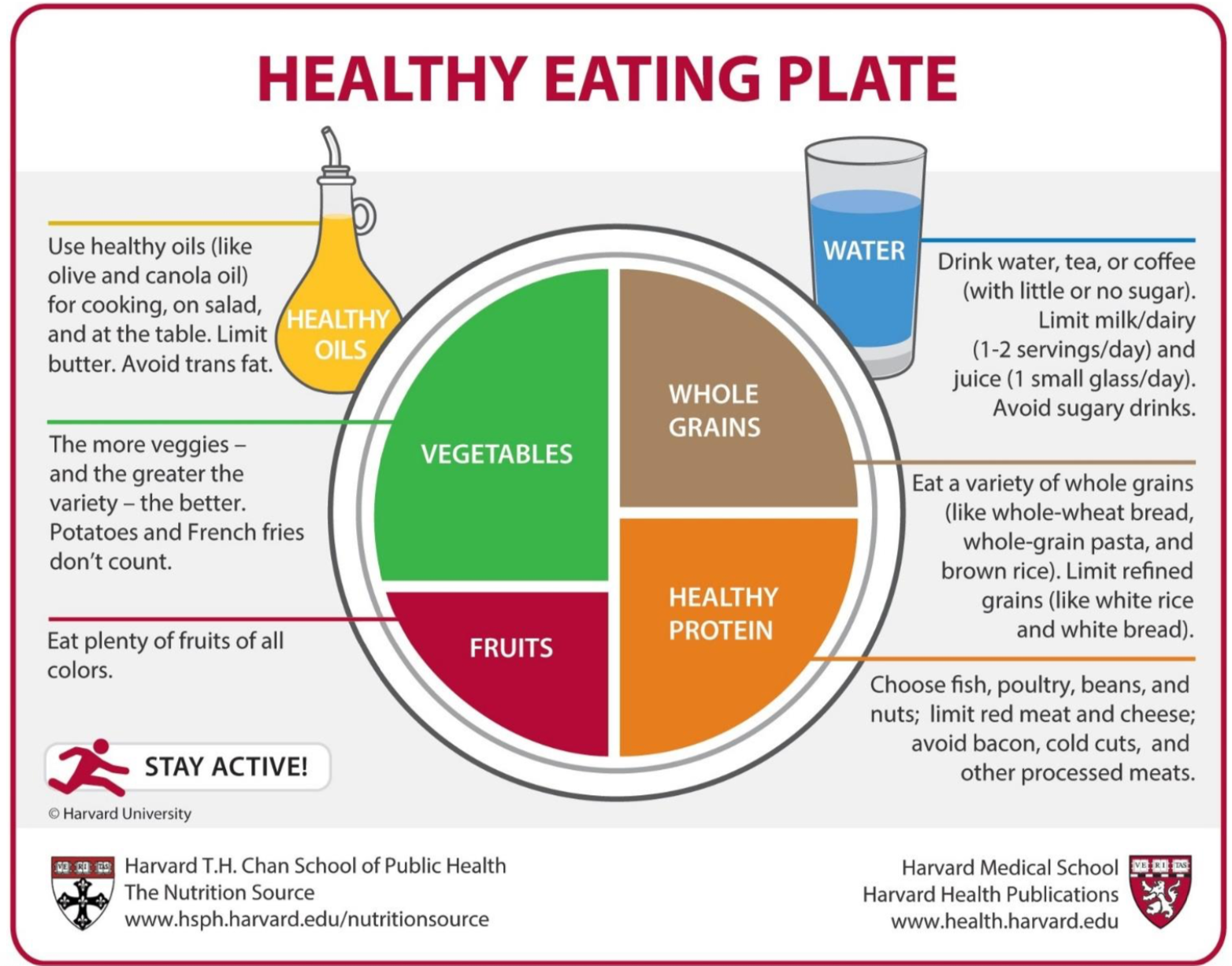
Step 1: Fill half your 9-inch plate with non-starchy vegetables
- Non-starchy vegetables are low in calories and carbohydrates and high in fiber. This means they can help you feel more full and satisfied with your meal, but won't lead to weight gain and high blood sugar.
- Aim for 1 to 2 cups of any vegetable, other than the starchy vegetables listed in Step 3.
- Vegetables can be raw or cooked.
Step 2: Limit protein to a quarter of your plate
- Choose lean meat, poultry or fish. Your portion should not be bigger than the palm of your hand. Try 1 to 2 whole eggs, or just use the egg whites for lower cholesterol.
- Choose tofu, nuts or seeds. Aim for about 2 tablespoons of nuts and seeds or 1/2 cup of tofu.
Step 3: Limit starch to a quarter of your plate
- Starch is a source of carbohydrate, which turns into an important fuel, called glucose. Limiting the portion size of starch helps control body weight and blood sugar.
- Choose a bun, tortilla, bread, bagel, rice, grains, cereal, pasta or a starchy vegetable.
- If you choose bread, limit it to 2 slices or 1/2 bagel.
- If you choose a hamburger or hotdog bun, limit it to 1 bun.
- If you choose a tortilla, limit it to 2 small tortillas or 1 large tortilla.
- If you choose rice, grains, pasta, cereal or a starchy vegetable, limit the portion to no more than 1 cup — this is about the size of a woman's fist. Starchy vegetables include beans, potatoes, corn, yams, peas
and winter squash.
- Choose most of your starches from whole grains, such as
whole wheat bread or tortillas, brown rice, whole grain and bran cereals, whole wheat pasta or beans.
NOTE: For a high-protein, low-carbohydrate diet, replace the starchy vegetable with more non-starchy vegetables, make the protein portion larger (4 to 6 ounces of lean meat or other protein rather than 2 to 4 ounces), and take a multivitamin and mineral supplement
Step 4: If desired, add one portion of fruit or milk
- Fruit, milk
and yogurt are also sources of carbohydrate. To best control body weight and blood sugar, limit yourself to either fruit or milk at your meal. You may choose to save the fruit or milk for a snack. - Because high-carbohydrate drinks can quickly raise blood sugar, avoid drinking fruit juice.
- Examples of fruit portions are:
- 1 small apple, orange, peach, pear, banana or nectarine, or half of a larger-size fruit
- 3/4 cup fresh pineapple chunks, blueberries or blackberries
- 17 grapes
- 1-1/4 cups strawberries or watermelon
- 1 cup cantaloupe, honeydew or papaya
- Choose low-fat or non-fat dairy products for heart health and weight control.
- Examples of milk and yogurt portion sizes are:
- 1 cup (8 ounces) of non-fat or 1 percent milk, or soy milk
- 2/3 to 1 cup plain non-fat or aspartame-sweetened fruit yogurt
Step 5: Limit added fats
- Avoid adding fats like butter, margarine, shortening, mayonnaise, gravies, cream sauces, salad dressing and sour cream to your food. Instead, season foods with herbs and spices.
- Cook using low-fat methods such as baking, steaming, broiling or grilling. Avoid frying foods.
Body Mass Index (BMI)
Maintaining a healthy weight is important for people with lung disease. Excess weight can increase shortness of breath and puts a strain on your heart. It can also lead to serious health problems such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, high blood pressure
A good way to assess your weight is to calculate your body mass index (BMI). BMI is a measure of body fat based on height and weight, and it applies to both adult men and women. You can calculate your BMI with this printable table from the National Institutes of Health, or use UCSF's online BMI calculator.
You should aim for a BMI of around 20 to 30. Certain groups may need to keep the following in mind when calculating their BMI:
Body builders — Because muscle weighs more than fat, people who are unusually muscular may have a higher BMI.- Elderly — It's often healthier for the elderly to have a BMI between 25 and 27, rather than lower than 25. If you're older than 65, for example, a slightly higher BMI may help protect you from osteoporosis.
- Children — This BMI information and table applies to adults only. Talk to your child's doctor about what's an appropriate weight for your child's age.
Increasing Protein in Your Diet
Ways to Add Protein to Your Diet
Milk:
- Drink a glass of milk with a snack.
- Add powdered milk to regular milk to drink or add to any recipe calling for milk, such as pudding, macaroni
and cheese, mashed potatoes, custard or casserole.
Cheese:
- Add cheese to sandwiches, toast, tortillas
and crackers. Melt cheese on vegetables, pastaand meat. - Have a bowl of chili with melted cheddar cheese.
- Make a pasta dish with ricotta cheese and sauce,
melt mozzarella on top and sprinkle with parmesan cheese. - Mix cottage cheese with fresh or canned fruit.
Yogurt:
- Have yogurt as a snack; add some nuts or seeds for extra protein.
Poultry and Fish:
- Chop chicken or turkey into small pieces and add two to three ounces to each serving of soup.
- Eat chicken salad as an entree, in a sandwich or on crackers.
- Add ground turkey or beef to spaghetti sauce of chili.
- Have a tuna fish sandwich or just a can of tuna fish as part of your lunch.
Eggs:
- Eat hard-boiled eggs as snacks.
- Eat deviled eggs.
- Make an omelet with whole eggs or egg whites and add shredded cheese, chopped meats
and vegetables. You will get less saturated fat with egg whites but you need two egg whites to equal the amount of protein in one whole egg.
Nuts and Nut Butters:
- Have a peanut butter and jelly sandwich or eat peanut butter mixed with a banana.
- Add chopped or ground nuts to muffins, pancakes, milkshakes, stir-fry or other meals and snacks.
Tofu:
- Make a milkshake or pudding pie with silken tofu.
Beans and Legumes:
- Make a bean dip: Layer refried beans, cheese, sour cream, guacamole
and other desired ingredients, and eat as is or with chips. - Eat hummus with pita bread, vegetable sticks or crackers.
Supplemental Drinks:
- Consume supplemental drinks such as Ensure or Boost Plus. The "plus" versions have about 6 to 8 more grams of protein than the regular kind.
All of these ideas can be adjusted to decrease
High-Protein Foods
The amount of protein in common foods is listed below. A good shortcut is that one ounce of meat or fish has about 7 grams of protein.
Beef
- Hamburger patty, 4 ounces — 28 grams
- Steak, 6 ounces — 42 grams
- Most cuts of beef — 7 grams of protein per ounce
Chicken
- Chicken breast, 3.5 ounces — 30 grams
- Chicken thigh, average size — 10 grams
- Drumstick — 11 grams
- Wing — 6 grams
- Chicken meat, 4 ounces cooked — 35 grams
Pork
Pork chop , average size — 22 grams- Pork loin or tenderloin, 4 ounces — 29 grams
- Ham, 3 ounces — 19 grams
- Ground pork, 3 ounces cooked — 22 grams
- Bacon, 1 slice — 3 grams
- Canadian-style bacon (back bacon), slice — 5 to 6 grams
Eggs and Dairy
- Egg, large — 6 grams
- Milk, 1 cup — 8 grams
- Cottage cheese, 1/2 cup — 15 grams
- Yogurt, 1 cup — usually 8 to 12 grams
- Soft cheeses (Mozzarella, Brie, Camembert) — 6 grams per ounce
- Medium cheeses (Cheddar, Swiss) — 7 or 8 grams per ounce
- Hard cheeses (Parmesan) — 10 grams per ounce
Beans (including soy)
- Tofu, 1/2 cup — 20 grams
- Tofu, 1 ounce — 2.3 grams
- Soy milk, 1 cup — 6 to 10 grams
- Most beans (black, pinto, lentils, etc) — about 7 to 10 grams protein per half cup of cooked beans
Soy beans , 1/2 cup cooked — 14 grams- Split peas, 1/2 cup cooked — 8 grams
Nuts and Seeds
- Peanut butter, 2 tablespoons — 8 grams
- Almonds, 1/4 cup — 8 grams
- Peanuts, 1/4 cup — 9 grams
- Cashews, 1/4 cup — 5 grams
- Pecans, 1/4 cup — 2.5 grams
- Sunflower seeds, 1/4 cup — 6 grams
- Pumpkin seeds, 1/4 cup — 19 grams
- Flax seeds, 1/4 cup — 8 grams
Fish
- Most fish
filets or steaks — about 6 grams per ounce - Tuna, 6-ounce can — 40 grams
Tips for Gaining Weight
People with chronic lung disease use lots of energy to breathe — they can burn 10 times more calories just breathing than someone without chronic lung disease. To prevent unwanted weight loss, follow the guidelines below, as well as those in the General Guidelines for Eating Healthy with Chronic Lung Disease. In addition to preventing weight loss, proper nutrition helps prevent infection, facilitate breathing and maintain a healthy respiratory system.
- Eat a high-calorie, high-protein diet. Concentrate on foods that are calorie-dense but healthy. See our sample week's high-calorie, high-protein meal plan for ideas.
- Add an extra 250 to 500 calories per day. This is how much people losing weight need. See our recipes for high-calorie, healthy snacks to get ideas for how to add these additional calories to your diet.
- Avoid drinking lots of fluids with meals. Fluids may make you feel full and prevent you from consuming the calories you need.
- Consume a high-calorie nutritional drink. Nutritional beverages such as Ensure or Boost can help add healthy calories to your diet.
If you're still not getting enough calories, take a multivitamin and mineral supplement.
High-Calorie and High-Protein Meals
Each meal below has between 400 to 600 calories.
|
Breakfast |
Lunch |
Dinner |
|
|
Day 1 |
1 cup cereal |
|
1 cup turkey chili |
|
Day 2 |
2 slices |
4 |
|
|
Day 3 |
3 eggs scrambled with: |
Macaroni and cheese: |
4 ounce grilled salmon |
|
Day 4 |
1 6-ounce yogurt |
1 slice pizza with meat |
Spaghetti with meatballs: |
|
Day 5 |
3 eggs scrambled with |
1 large (4-ounce) bagel |
Burrito: |
|
Day 6 |
2 slices French toast |
2 slices |
4-ounce hamburger on |
|
Day 7 |
Breakfast Burrito: |
1, 4-ounce bagel |
4 ounces grilled chicken |
Snacks and Desserts
To get 2,000 calories daily, add two choices from the list below to the sample menu. For 2,500 calories daily, eat three choices from the list below.
|
Snacks |
Desserts |
|
Smoothie: 1 cup whole milk, 1 scoop protein powder, 1 cup fruit |
1/2 cup ice cream, 1 Tbsp chocolate sauce, 1/4 cup nuts, 1 Tbsp whipped cream |
|
6 ounces 2% yogurt, 1/2 cup fiber cereal |
Milkshake: 1 cup whole milk, 1/2 cup ice cream, 2 tbsp chocolate syrup |
|
6 crackers |
1/2 cup ice cream |
|
10 almonds |
1 envelope Carnation Instant Breakfast prepared with 1 cup whole milk |
|
Protein bar |
6 graham crackers |
|
10 corn chips |
4 cookies |
|
1 apple |
1 brownie |
|
3 cups of popcorn with butter |
1 slice pie |
|
1 |
1/2 cup ice cream |
Tips for Losing Weight

People with chronic lung disease may gain weight for many reasons, such as poor diet, medications and lack of exercise because of shortness of breath. This weight gain can be stopped by following the guidelines below, in addition to those in the General Guidelines for Healthy Eating.
Eat a high-protein, low-carbohydrate diet. There is some evidence that this kind of diet may decrease appetite.
Eat carbohydrates in the form of fresh fruits and vegetables, not "simple" carbs. Simple carbohydrates and concentrated sweets, such as cakes, pies, cookies, jams, honey, chips,
Limit saturated fat and cholesterol. Choose lean meats, poultry
Eat small, frequent meals. This will help satisfy your appetite and make breathing easier than if you eat large meals.
Watch portion size.
You can also print and cut out this Serving Size Card from the National Institutes of Health, as a guide for healthy portion sizes.
Use the plate method to plan healthy meals. It can be modified to fit a high-protein, low-carbohydrate diet.
Exercise regularly as advised. Daily walking, working out at a gym and participating in pulmonary rehabilitation burn calories and help you maintain function, strength
Seek support. You can find support at your local hospital's weight management program, or through organizations such as Weight Watchers.
Prednisone and Weight Gain
Weight gain is a common side effect of prednisone. Prednisone can also cause a redistribution of fat to the face, back of the neck and the abdomen, although these changes vary from person to person. Generally speaking, the higher the dose and the longer the treatment, the greater the changes.
Weight gain while taking prednisone is typically due to fluid retention and increased calorie intake because of increased appetite. In addition, those with lung disease have more difficulty maintaining physical activity.
Fluid Retention
Fluid retention can be controlled by eating a diet low in sodium — no more than 2,000 mg a day — and higher in potassium. You can find a list of high-sodium foods to avoid in the General Guidelines for Healthy Eating.
You can increase your potassium intake by eating potassium-rich foods such as:
- Apricots
- Baked potatoes
- Bananas
- Cantaloupe, honeydew
- Dates
- Dried prunes
- Grapefruit
- Lima beans
- Milk
- Orange juice, grapefruit juice
- Oranges
- Raisins
- Spinach, cooked
- Stewed tomatoes
- Tomato juice
- Winter squash
- Yogurt
Increased Calorie Intake
Prednisone increases appetite, resulting in increased calorie intake. This increased appetite can be difficult to control. Below are a few tips for controlling the
Eat small, frequent meals of high nutritional value.
Eat a high-protein, low-carbohydrate diet. There is evidence that a low-carbohydrate, high-protein diet is at least as effective for losing weight as a traditional low-calorie diet that's low in fat and portion-controlled. A high-protein diet may also help suppress appetite.
Eat carbohydrates in the form of fresh fruits and vegetables. Prednisone has a tendency to raise the level of glucose, or sugar, in the blood, which can cause increased body fat or diabetes in some people. It is important to avoid "simple" carbohydrates and concentrated sweets, such as cakes, pies, cookies, jams, honey, chips, bread, candy
Limit saturated fat and cholesterol. Choose lean meats, poultry
Eat foods rich in calcium. Prednisone may alter your body's ability to use calcium. Try to get four servings of calcium-rich foods per day to help prevent osteoporosis. Check with your doctor to see if you would benefit from calcium supplements.
Foods rich in calcium include:
- Calcium-fortified orange juice
- Cheese (American, Swiss, Colby, Cheddar and Jack)
- Cottage cheese
- Milk
- Non-fat dry milk powder
- Oranges
- Sardines (canned, with bones)
- Shrimp
Yoghurt
Decreased Physical Activity
Having a lung disease makes physical activity more difficult. A daily exercise program such as walking, working out at a gym or at home or practicing tai chi will burn calories, help prevent muscle and bone loss and improve your sense of well-being.
Your exercise program should include aerobic exercises, which burn calories and improve cardiovascular fitness, and moderate weight training, which strengthens muscles and slows bone loss. Start with a simple walking program. If you're ever too fatigued to exercise, try harder tomorrow. Eat your main meal early in the day so you'll have more energy throughout the day and if you need it, be sure to wear your oxygen.
The key is to have a program of regular exercise. A pulmonary rehabilitation program is an excellent way to learn how to exercise despite
For more information on eating healthy with chronic lung disease, please see our General Guidelines.
Diet Recommendation for Medication Side Effects
Medications prescribed for ILD are sometimes associated with gastrointestinal side effects. Below are some tips on how to manage some of these side effects.
Diarrhea
- Eat smaller meals frequently throughout the day.
- Include sources of soluble fiber to absorb excess water in stools.
- Avoid greasy, fatty, and fried foods.
- Avoid concentrated sweets such as candy, cakes, cookies, and muffins.
- Avoid sweet or sugary drinks such as fruit juices, soft drinks and sodas.
- Avoid foods that cause you gas and cramping.
- Drink fluids between meals. Diarrhea can cause dehydration. Drink liquids such as water, broth, sports beverages, Gatorade, and popsicles.
- Avoid foods and drinks that can have a laxative effect. Examples include prunes, prune juice and apple juice.
- Drink milk if it is a regular part of your diet. Some individuals will experience temporary lactose intolerance during a phase of acute diarrhea.
- Avoid the use of straws, as they can introduce unnecessary gas and cramping.
Nausea
- Eat regular
meals 5-6 per day. Having some food in your stomach may help you feel better. - Try dry Saltine-style crackers, toast, natural potato chips, and pretzels.
- Keep crackers at your bedside if nausea is a problem in the morning or after a nap.
- Try foods that are easy on your stomach, such as oatmeal, rice, or cream of wheat, boiled potatoes or noodle
- Low-fat protein sources such as skinned chicken or tofu that is baked or broiled, not fried
- Peaches or other soft, mild-tasting fruits and vegetables
- Clear liquids such as apple and cranberry juice, low-salt broth, and carbonated drinks without caffeine
- Teas such as ginger and peppermint, served lukewarm or cold.
- Slowly drink or sip liquids throughout the day.
- Stay away from odors. Have someone else cook if possible. Eat in the dining room or in a room other than the kitchen.
- Try colder foods and main-dish salads. Avoid hot foods and hot liquids.
- Track your nausea by taking note of any particular food or events that trigger it. See if there is a pattern, and if so, try to change that pattern.
- Stay quiet after meals. Try to rest while sitting up for about an hour – you can watch TV, read a magazine, talk with a loved one, or enjoy the company of your pet.
- Avoid fried, greasy, and rich foods.
- Don't force yourself to eat your favorite foods when you feel nauseated, as you may develop a dislike for these foods.
Loss of appetite and weight loss
- Eat by the clock rather than by your hunger mechanism.
- Snack between meals.
- Make every bite count.
- Plan for special circumstances.
- Plan your daily menu in advance.
- Request help in preparing your meals.
- Fix several portions of your favorite foods and freeze them.
- Make food visually appealing.
- Appeal to your sense of smell.
- Make your mealtimes pleasant.
- High calorie shakes between meals: some examples include those made by Ensure, Boost, Carnation Instant Breakfast, Orgain, Kate Farm, or your own home-made shakes!
